
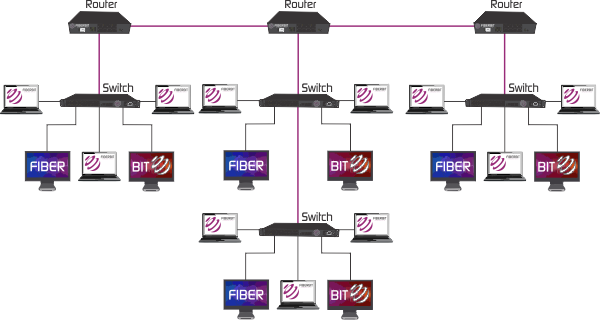
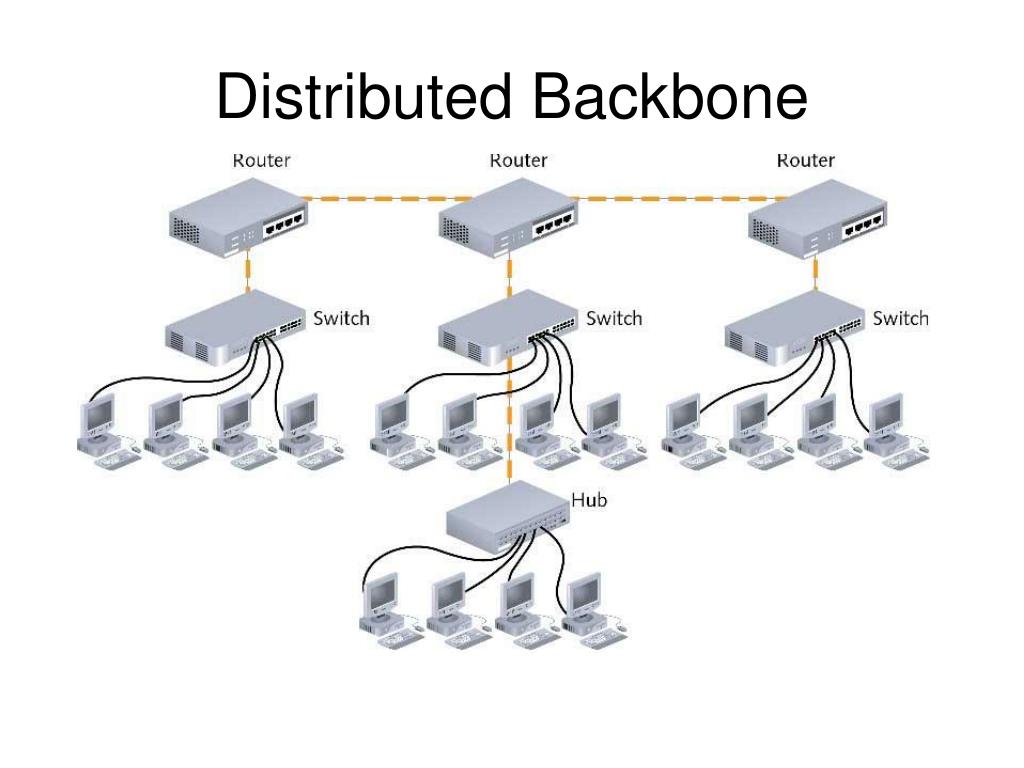
In case a message has to be sent over the network, the message is put all over the network. Every node of the network is either connected to the backbone cable by drop cable or directly to the backbone cable. In Bus Topology, all the stations are connected through a single cable known as a backbone cable. Here in this section, we have discussed all the topologies in detail along with their advantages. There are 6 types of Topologies in computer networks namely Bus, Tree, Mesh, Ring, Star and Hybrid Topology.

Network Topology is the arrangement of a network that comprises nodes and connecting lines via sender and receiver. The structure of the network of how all the various elements such as links, nodes, etc of a computer network are interconnected to each other is defined as Topology in Computer Network. The network topology can be classified into two categories-ġ) Physical Topology: The placement of the various components of a network including device location, cable installation, etc is known as Physical Topology.Ģ) Logical Topology: The illustration of the flow of data within a network regardless of the Physical design is termed as Logical Topology.

Adjust the placement, size, color, and other attributes of your diagram elements until you’re satisfied.įor a more in-depth look at making network diagrams, including additional tips and tricks, check out this tutorial.There are various ways through which different components are connected to one another in Computer Networks. You may choose to place that information next to each component or to number the components, then add additional info in a legend. Include any additional information about each shape that you consider useful to your audience. A line between two shapes shows that they are connected somehow, typically by the flow of information. Shapes may be related either logically or physically, depending on what kind of diagram you’re drawing. To begin arranging your diagram, move related shapes closer to one another.
If you’re using network diagramming software, you can accomplish this by simply dragging shapes onto the canvas. Instead, just list all the workstations, servers, routers, firewalls, and other components that are part of the network. Once you’ve selected a network to map, follow these steps to produce a beautiful, useful network diagram. It’s better to create multiple diagrams, each capturing a different aspect of the network, than it is to try to cram all the information onto one diagram.
#BACKBONE NETWORK TOPOLOGY EXAMPLES PROFESSIONAL#
Planning the structure of a home or professional network.With their capacity for showing how network components interact, network diagrams can serve a variety of purposes, including: Typically, the diagram gives a bird’s eye view of the network in its physical space, like a floorplan. Physical network diagramsĪ physical network diagram shows the actual physical arrangement of the components that make up the network, including cables and hardware. Level 2 shows the data links between adjacent nodes, while level 1 shows the purely physical layout. Also known as the “network layer,” 元 is an abstraction layer that deals with packet forwarding through intermediate routers. In the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model, logical network diagrams correlate with the information contained in layer 3 (元).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
